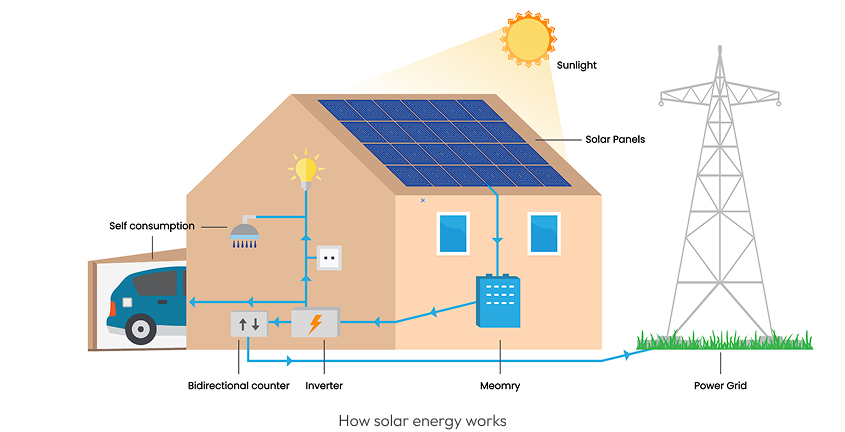
Solar energy works through several innovative technologies.
1. Photovoltaic (PV) systems
These systems use solar panels made of semiconductor materials that convert sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight strikes the PV cells, electrons are set into motion, generating direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts this DC into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for home or commercial use.
2. On-Grid solar systems
These systems are known as grid-tied systems, which are connected to the public electricity grid. Excess energy generated by your solar panels can be fed back into the grid, often earning you credit via net metering. This system ensures that you always have power, even when the sun isn’t shining, by drawing from the grid when needed.
3. Off-Grid solar systems
Off-grid systems operate independently of the public electricity grid. They typically include battery storage, which stores excess energy for use during cloudy days or at night. These systems are ideal for remote areas where grid connectivity is limited or nonexistent.
4. Solar thermal systems
Instead of converting sunlight directly into electricity, solar thermal systems capture the sun’s heat to warm water or air. This heat can then be used for residential heating, hot water, or even industrial processes.
Understanding these various systems helps answer the question of what solar energy is by demonstrating its versatility. From powering a single house to lighting up communities in different parts of the world.