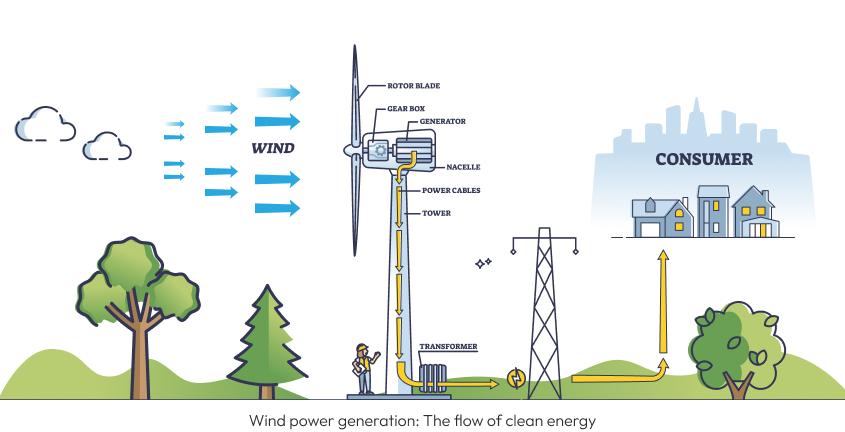
While we’ve all seen these beautiful giants touching the sky, the question remains—how do they capture energy?
Wind turbines generate electricity by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into usable electrical energy. Here’s an insight into their functioning:
1. Wind turns the blades
The blades are designed with an aerodynamic shape like airplane wings, which enables them to capture the energy of the wind effectively. As the wind pushes against the blades, they begin to spin, and kinetic energy is created.
2. Rotation of the shaft
The blades are connected to a rotor, which is further connected to a shaft inside the turbine's nacelle. As the blades rotate, they cause the shaft to spin as well.
3. Powering the generator
The rotating shaft is connected to a generator inside the nacelle. This generator transmits and transforms the energy from the shaft to produce electrical energy. This process, known as electromagnetic induction, involves a dynamic interaction between magnets and coils that generates current.
4. Excess energy export
If the solar panels generate more electricity than the home consumes, the surplus is exported to the local electricity grid. This process is facilitated by a bi-directional meter that tracks both the energy consumed from the grid and the energy supplied back to it.
5. Electricity is generated
The generator produces alternating current (AC) electricity. This electricity is passed through a transformer located on-site, which increases the voltage to match the requirements of the national grid.
6. Electricity is supplied to the grid
Once the voltage is increased, the electricity is transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries. This is how electricity from wind is fed into the grid for general use.